آموزش میکروکنترلر STM32F4 : ابزارهای ارتباطی بین Thread ها
قسمت 12
در قسمت یازدهم آموزش میکروکنترلر STM32F4 به ادامه RTOS و مباحث سمافور و موتکس پرداختیم. در این قسمت از آموزش میکروکنترلر STM32F4 به ابزارهای ارتباطی بین Thread ها میپردازیم. با سیسوگ همراه باشید.
ابزارهای ارتباطی بین Thread ها
ابزارهایی که برای ارتباط بین Threadها در دسترس است، عبارتند از صفهای نامه، صفهای پیام، سیگنالها و حوضچه حافظه. در زیر این ابزارها بررسی میشود.
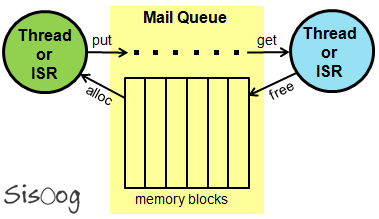
صف نامه
تابع مدیریت صفِ نامه (Mail Queue) اجازه میدهد که فرستادن، دریافت، انتظار یا کنترل نامهها ممکن شود. یک نامه، بلوکی از حافظه است که به یک Thread یا روال وقفه فرستاده میشود.
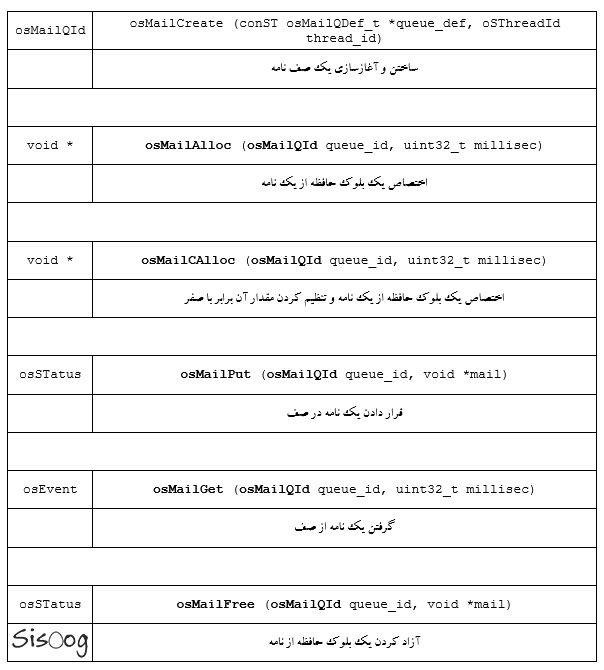
ماکروهای تعریف شده

تابع های تعریف شده
همانطور که در برنامه زیر دیده میشود برای انتقال دادهها بین دو Thread از صف نامه (صندوق نامه) استفاده شده است. یک Thread دادههایی را در نامه قرار میدهد و می فرستد و Thread دیگر که همواره منتظر دریافت است با دریافت نامه آن را چاپ میکند.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 |
#include "cmsis_os.h" oSThreadId tid_thread1; // ID for thread 1 oSThreadId tid_thread2; // ID for thread 2 typedef STruct { // Mail object STructure float voltage; // AD result of measured voltage float current; // AD result of measured current int counter; // A counter value } T_MEAS; osMailQDef(mail, 16, T_MEAS); // Define mail queue osMailQId mail; void send_thread (void conST *argument); // forward reference void recv_thread (void conST *argument); oSThreadDef(send_thread, osPriorityNormal, 1, 0); // thread definitions oSThreadDef(recv_thread, osPriorityNormal, 1, 2000); /* Thread 1: Send thread */ void send_thread (void conST *argument) { T_MEAS *mptr; mptr = osMailAlloc(mail, osWaitForever); // Allocate memory mptr->voltage = 223.72; // Set the mail content mptr->current = 17.54; mptr->counter = 120786; osMailPut(mail, mptr); // Send Mail osDelay(100); mptr = osMailAlloc(mail, osWaitForever); // Allocate memory mptr->voltage = 227.23; // Prepare 2nd mail mptr->current = 12.41; mptr->counter = 170823; osMailPut(mail, mptr); // Send Mail oSThreadYield(); // Cooperative multitasking // We are done here, exit this thread } /* Thread 2: Receive thread */ void recv_thread (void conST *argument) { T_MEAS *rptr; osEvent evt; for (;;) { evt = osMailGet(mail, osWaitForever); // wait for mail if (evt.STatus == osEventMail) { rptr = evt.value.p; printf ("\nVoltage: %.2f V\n", rptr->voltage); printf ("Current: %.2f A\n", rptr->current); printf ("Number of cycles: %d\n", rptr->counter); osMailFree(mail, rptr); // free memory allocated for mail } } } void STartApplication (void) { mail = osMailCreate(osMailQ(mail), NULL); // create mail queue tid_thread1 = oSThreadCreate(oSThread(send_thread), NULL); tid_thread2 = oSThreadCreate(oSThread(recv_thread), NULL); : } |
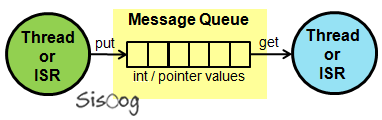
صف پیام
تابعهای مدیریتِ صف نامه ( Message Queue )، کنترل، فرستادن، دریافت یا منتظر ماندن برای یک پیام را ممکن میکنند. یک پیام میتواند یک عدد صحیح یا یک اشارهگر باشد که به Thread، یا روال وقفه فرستاده میشود.
ماکروهای تعریف شده

تابعهای تعریف شده

در کد زیر مثالی از به کاربردن صف پیام دیده میشود.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 |
#include "cmsis_os.h" oSThreadId tid_thread1; // ID for thread 1 oSThreadId tid_thread2; // for thread 2 typedef STruct { // Message object STructure float voltage; // AD result of measured voltage float current; // AD result of measured current int counter; // A counter value } T_MEAS; osPoolDef(mpool, 16, T_MEAS); // Define memory pool osPoolId mpool; osMessageQDef(MsgBox, 16, T_MEAS); // Define message queue osMessageQId MsgBox; void send_thread (void conST *argument); // forward reference void recv_thread (void conST *argument); // forward reference // Thread definitions oSThreadDef(send_thread, osPriorityNormal, 1, 0); oSThreadDef(recv_thread, osPriorityNormal, 1, 2000); /* Thread 1: Send thread */ void send_thread (void conST *argument) { T_MEAS *mptr; mptr = osPoolAlloc(mpool); // Allocate memory for the message mptr->voltage = 223.72; // Set the message content mptr->current = 17.54; mptr->counter = 120786; osMessagePut(MsgBox, (uint32_t)mptr, osWaitForever); // Send Message osDelay(100); mptr = osPoolAlloc(mpool); // Allocate memory for the message mptr->voltage = 227.23; // Prepare a 2nd message mptr->current = 12.41; mptr->counter = 170823; osMessagePut(MsgBox, (uint32_t)mptr, osWaitForever); // Send Message oSThreadYield(); // Cooperative multitasking // We are done here, exit this thread } /* Thread 2: Receive thread */ void recv_thread (void conST *argument) { T_MEAS *rptr; osEvent evt; for (;;) { evt = osMessageGet(MsgBox, osWaitForever); // wait for message if (evt.STatus == osEventMessage) { rptr = evt.value.p; printf ("\nVoltage: %.2f V\n", rptr->voltage); printf ("Current: %.2f A\n", rptr->current); printf ("Number of cycles: %d\n", rptr->counter); osPoolFree(mpool, rptr); // free memory allocated for message } } } void STartApplication (void) { mpool = osPoolCreate(osPool(mpool)); // create memory pool MsgBox = osMessageCreate(osMessageQ(MsgBox), NULL); // create msg queue tid_thread1 = oSThreadCreate(oSThread(send_thread), NULL); tid_thread2 = oSThreadCreate(oSThread(recv_thread), NULL); : } |
سیگنالها
تابعهای مدیریت سیگنال امکان کنترل یا انتظار برای پرچمهای سیگنال را فراهم میکند. که به هر Thread دارای پرچمهای سیگنال اختصاص داده شده است.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
#include "cmsis_os.h" DigitalOut led(LED1); void led_thread(void conST *args) { while (true) { // Signal flags that are reported as event are automatically cleared. osSignalWait(0x1, osWaitForever); led = !led; } } oSThreadDef(led_thread, osPriorityNormal, DEFAULT_STACK_SIZE); int main (void) { oSThreadId tid = oSThreadCreate(oSThread(led_thread), NULL); while (true) { osDelay(1000); osSignalSet(tid, 0x1); } } |
حوضچه حافظه
حوضچههای حافظه، بلوکهای حافظه پویا هستند که توسط سیستم عامل مدیریت میشوند و بنابراین Thread امن هستند. از حافظه heap سریعتر هستند و مشکل قطعه قطعه شدن را نیز ندارند. از این حافظهها میتوان در Threadها و روالهای وقفه استفاده کرد. با این گامها میتوان حوضچههای حافظه را ساخت و از آنها استفاده کرد.
در قسمت سیزدهم آموزش میکروکنترلر STM32F4 به مبحث تایمرها خواهیم پرداخت. با سیسوگ همراه باشید.















سیسوگ با افتخار فضایی برای اشتراک گذاری دانش شماست. برای ما مقاله بنویسید.